



04:39:25 14/11/2024
What is Periapical Inflammation?
Periapical inflammation occurs when the tooth pulp dies, leading to an infection in the surrounding area of the tooth root, such as the alveolar bone and periodontal ligaments. Bacteria from the inflamed pulp spread, causing swelling, pain, and potentially leading to many serious complications.
Causes of Periapical Inflammation
Periapical inflammation is typically caused by three main factors: bacterial infection, dental trauma, and treatment errors.
1. Bacterial infection
Bacteria from a cavity can enter the pulp, causing pulpitis, which eventually spreads down to the root area, causing infection. These bacteria release toxins (such as protein-digesting enzymes, prostaglandins) that damage and inflame the root area.
2. Dental trauma
Dental trauma can be chronic (due to teeth grinding, malocclusion) or acute (from a blow, biting on hard objects). Both types of trauma can damage the tissues around the root and increase the risk of infection.
3. Treatment errors
Errors during endodontic (root canal) treatment, such as blocked root canals, allergies to filling materials, or excess filling materials, can irritate and inflame the root area.
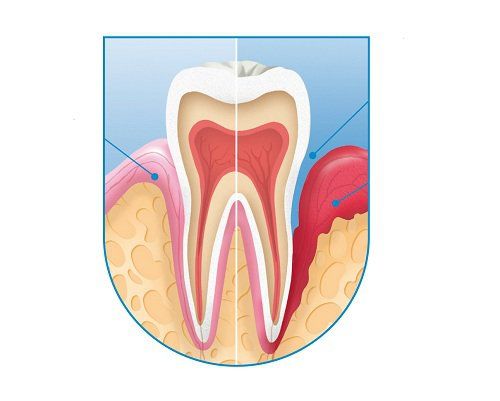
Complications of Periapical Inflammation
If periapical inflammation is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Formation of an abscess in the infected area.
- Bacteria spreading and causing inflammation in the jawbone.
- Persistent fever caused by the infection.
- Bad breath and discomfort during chewing.
- Severe cases may result in tooth loss.
- Bacteria from the mouth may enter the stomach and digestive system, causing further health issues.
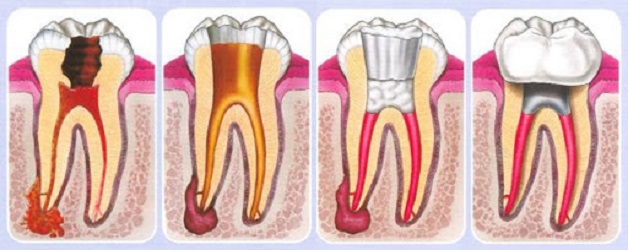
Treatment for Periapical Inflammation
For periapical inflammation, the doctor may prescribe the following treatments:
- Systemic Treatment: Use of antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor.
- Endodontic Treatment: Cleaning and shaping the root canal, applying a specialized solution to neutralize the tissues around the root, followed by disinfecting and sealing the canal to restore the tooth structure.
- Surgical Treatment: In cases where damage around the root cannot be corrected with the above methods, the doctor may remove the cystic lining, resect the root, and seal it to protect the root from external factors.
Prevention of Periapical Inflammation
To prevent periapical inflammation, you should follow these practices:
- Oral Hygiene: Brush teeth 2-3 times daily with a soft-bristled brush, using moderate force.
- Use Supporting Tools: Combine with floss, interdental brushes, specialized mouthwash, and saline solutions to thoroughly remove plaque and maintain fresh breath.
- Healthy Diet: Limit sugary foods, carbonated drinks, and stimulants such as alcohol, tobacco, tea, and coffee.
- Increase Vitamins, Fiber, and Minerals: Ensure adequate intake of vitamins, fiber, and minerals in your daily diet to strengthen teeth.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit the dentist every 6 months for early detection and treatment of cavities to prevent pulpitis or pulp death.
25/10/24

25/10/24
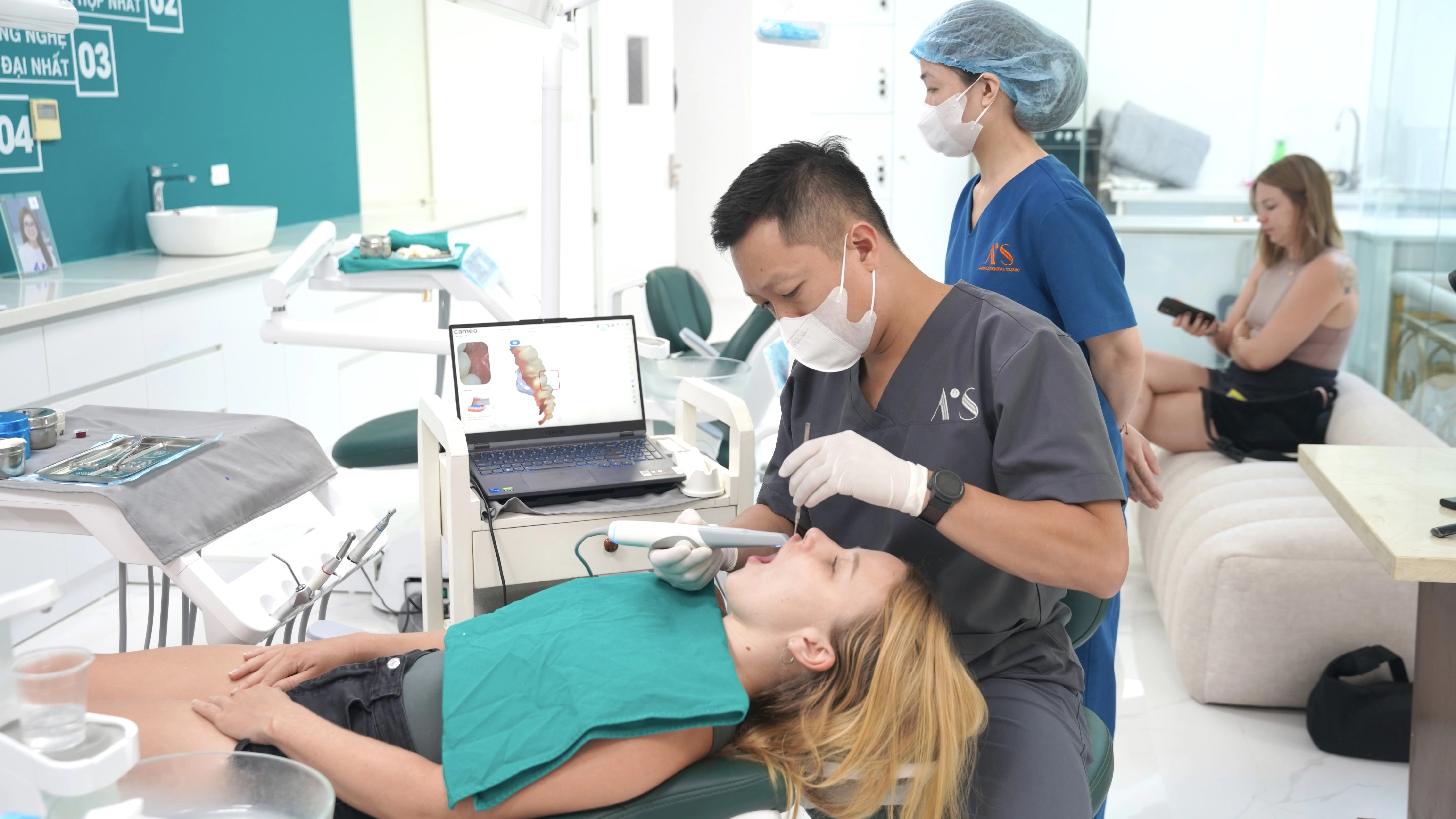
07/11/24
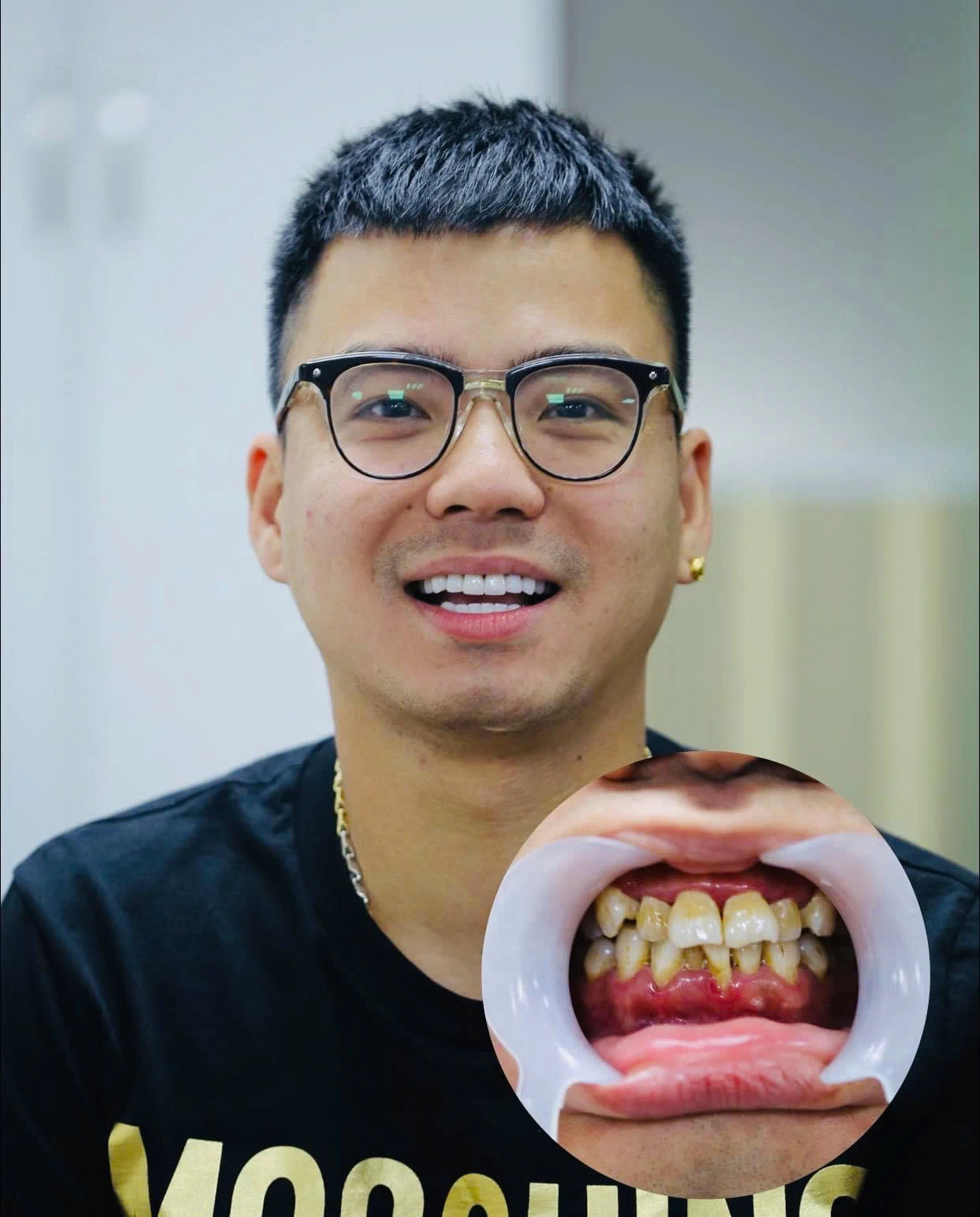
11/12/24

07/11/2024
Braces have become increasingly popular as an effective method to improve both the aesthetics and function of teeth. However, some people are concerned that this process may impact their speech abilities. So, does wearing braces actually affect speech? Let's explore this topic in detail with Amass.
Detail
02/11/2024
Caring for children's oral health from an early age is an important responsibility that parents cannot overlook. Tooth decay in molars is not only a common issue but can also have long-lasting effects on the development of their permanent teeth.
Detail
01/11/2024
In feng shui, the shape of one’s teeth can reflect personality and energy, influencing social relationships, work, and family dynamics. Features like sharp front teeth, misaligned teeth, or irregular growth are often seen as indicators of unstable energy, potentially generating conflicts. Below are some feng shui insights about sharp teeth and how they may impact your life:
Detail